Why is the video still blurry even though it is very large when it is uploaded to the video platform? There is a misunderstanding here, that we confuse the encoding and packaging of the video.
We need to understand first what information a video contains: image, audio, media information, and packaging.

The file suffixes are the packaging information. Mp4, mov, mkv, etc. are common packaging formats. You can think of it as a container for your video content, packaging your video and audio files together.
Here are some common packaging formats:
- AVI:
AVI, or Audio Video Interleave, is a file format for storing video and audio data. Microsoft developed it in the early 1990s as a way to store video and audio data in a single file, making it easier to share and playback multimedia content.
AVI files are often used for storing and playing back video on personal computers, as they are supported by a wide range of software, including media players and video editing programs. AVI files can contain audio and video data and other information such as subtitles and metadata.
AVI files use a variety of codecs to compress and encode the audio and video data. Some common codecs used in AVI files include DivX and XviD for video and MP3 and PCM for audio. Using codecs allows AVI files to be relatively small in size while still maintaining good quality.
AVI files can also be played back on many portable devices, such as smartphones and tablets, as well as on some TVs and DVD players. However, AVI files may not be as widely supported as other video file formats, such as MP4 or MOV.
- WMV:
WMV, or Windows Media Video, was developed by Microsoft as a way to store and playback video on personal computers running the Windows operating system.
WMV files are often used for storing and playing back video on personal computers, as they are supported by a wide range of software, including media players and video editing programs. WMV files can contain audio and video data and other information such as subtitles and metadata.
WMV files use a variety of codecs to compress and encode the audio and video data. Some common codecs used in WMV files include Windows Media Video and Windows Media Audio. Using codecs allows WMV files to be relatively small in size while still maintaining good quality.
WMV files can also be played back on some portable devices, such as smartphones and tablets, as well as on some TVs and DVD players. However, WMV files may not be as widely supported as other video file formats, such as MP4 or MOV.
- MOV
MOV is a video format developed by Apple and is commonly used for storing and playing back video on Mac computers and iOS devices. It is based on the QuickTime file format and is known for its ability to support a wide range of audio and video codecs, making it a good choice for storing high-quality video.
MOV files can be created using a variety of video and audio codecs, including H.264, H.265, and ProRes for video and AAC or MP3 for audio. This allows for a high level of flexibility in terms of the type of content that can be stored in a MOV file.
In addition to its support for a wide range of codecs, MOV files are also known for their ability to support multiple tracks of audio and video, making them a good choice for storing multimedia content such as movies and TV shows.
While MOV is primarily used on Apple devices, it is also supported by some other software and devices, such as Windows Media Player and VLC media player. However, it may not be as widely supported as other video formats, such as MP4 or AVI.
- MKV/OGG (open source)
MKV stands for Matroska Video, and it is an open-source container format for audio and video. It is a popular format for high-definition video and is often used for downloading and storing movies and TV shows. Ogg is a container format for audio and video that is designed to provide efficient streaming and manipulation of multimedia content. Ogg is an open, free-standing format that is designed to provide efficient streaming and manipulation of multimedia content.
MKV and Ogg are both container formats, which means that they are used to store audio, video, and other data in a single file. These formats allow for multiple audio and video tracks to be included in the same file, as well as for other data, such as subtitles and metadata, to be included.
Both MKV and Ogg are popular choices for storing and sharing video content, and they are supported by a wide range of media players. They are also both open, non-proprietary formats, which means that they are freely available for anyone to use.
- AVCHD (Panasonic/Sony)
AVCHD (Advanced Video Codec High Definition) is a video format developed by Sony and Panasonic for use in high-definition camcorders and digital cameras. It is designed to offer high-quality video while maintaining a relatively small file size, making it a good choice for storing and transmitting video content.
AVCHD files can be created using a variety of video and audio codecs, including H.264 and AVC for video and Dolby Digital or Linear PCM for audio. These codecs are designed to provide high-quality video while maintaining a small file size, making AVCHD a good choice for storing and transmitting video content.
AVCHD files are typically played using a media player or other software that supports the AVCHD format. This allows for the easy playback of AVCHD files on a wide range of devices, including computers, TVs, and home theater systems.
In addition to its use for storing and playing back video, AVCHD is also commonly used for creating and editing video content. It is a popular choice for professionals and enthusiasts who require high-quality video with a small file size.
- MP4
MP4, short for MPEG-4 Part 14, is known for its versatility and compatibility with a wide range of devices and software. One of the main advantages of MP4 is that it is based on the ISO base media file format, which makes it easy to store and transmit multimedia content, including audio, video, and text. MP4 files can be played on a wide range of devices, including smartphones, tablets, and computers, and are often used for streaming video on the internet.
MP4 files can be created using a variety of video and audio codecs, including H.264 and H.265 for video and AAC or MP3 for audio. This allows for a high level of flexibility in terms of the type of content that can be stored in an MP4 file.
In addition to its widespread compatibility and flexibility, MP4 is also known for its ability to offer high-quality video while maintaining a relatively small file size. This makes it a popular choice for storing and transmitting video content, particularly when file size is a concern.
Which packaging format is the most suitable?
Avi can be accepted by almost all software, but it is too old and does not support many modern video encodings, such as h264. Wmv, developed by Microsoft, only supports Microsoft encoding and is difficult to play on other operating systems. Mov has good compatibility with almost all encoding formats and can be played on different operating systems through QuickTime. Although mov was developed by Apple and is a packaging format biased towards Mac, mov is very worth considering. Mkv and ogg, as open source formats, have excellent compatibility with video encoding, but due to not being from a well-known source, their compatibility with different software varies. They are not recommended as the first choice here. AVCHD was created specifically for consumer-level camcorders and is packaged in a folder format, with media information and video stored separately. Once the order of the folder is disrupted, it is very likely to have problems when importing. Therefore, it is not suitable for sharing videos on the internet. Mp4 is the most perfect packaging format in the current environment. Mp4 has good cross-platform compatibility and also supports various modern encoding formats. If your video is going to be shared on the internet, be sure to choose mp4.
Now let’s look at what encoding is.
Video encoding is the science of reducing the size or bitrate of a video without negatively impacting its quality, as perceived by humans.
Reducing the size of a file is called compression, and video is compressed using a well-defined set of mathematical tools and algorithms (called video codecs). After a video has been compressed, it is typically in a format (called a bitstream) that can only be understood by software that can decode the corresponding bitstream. For example, a video encoded using the H.264/AVC video codec cannot be decoded by an HEVC codec, and vice versa.
A video codec is a set of tools and algorithms designed to compress video to achieve a predetermined rate-distortion tradeoff. Video codecs are typically built by consensus and involve committees of engineers, academics, and scientists from the industry (software and hardware companies).
The most commonly used encoding formats are lossy formats, and lossy formats are usually divided into two types: intraframe compression and interframe compression.
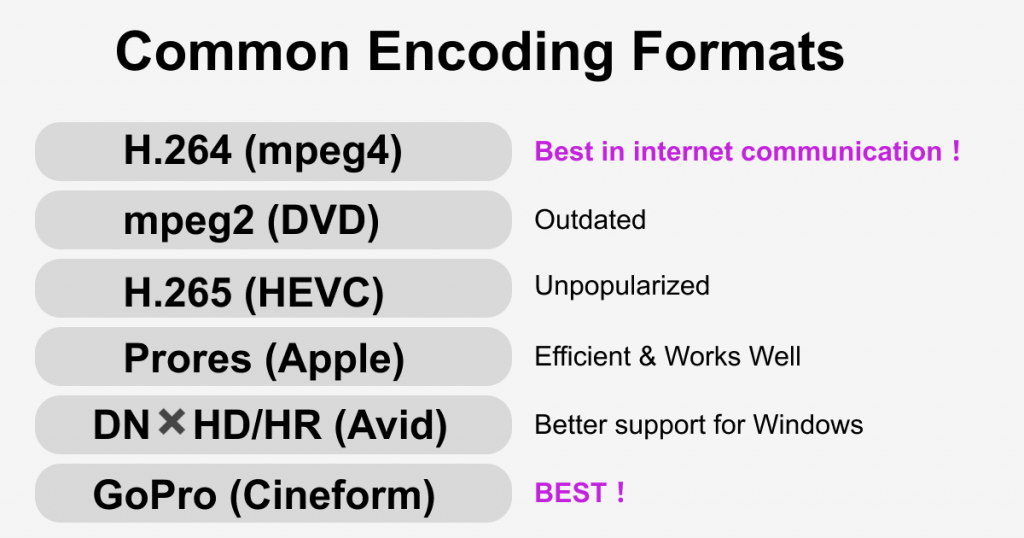
Interframe compression involves compressing multiple frames at the same time by comparing them. When encoding video, not all frames are stored, but rather keyframes are marked on the image, and the image between two frames is recalculated through computation when decoding. This method can obviously greatly reduce the size of the video, but the compression method has a lower image quality compared to intraframe compression. And decoding requires more computer resources. Common interframe compressions include H.264 (mpeg4), mpeg2 (DVD), and H.265 (HEVC).
Intraframe compression involves independent compression of each frame. For example, in a video, pixels with the same color are intelligently compressed. This format has a lower compression rate than interframe compression, but it can greatly reduce the load on the computer. Common intraframe compressions include Prores (Apple), DN✖️HD/HR (Avid), and GoPro Cineform.
Perhaps H.265 will be popular in the future, but for now, if you upload to the internet, choose H.264. Prores is also excellent, but more suitable for Mac. DN✖️HD/HR (Avid) is better supported on Windows. Cineform is extremely excellent and efficient and is also recommended.
Conclusion—
So, your video can be blurry even though it is very large when it is uploaded to the video platform. How to have high-quality, low-capacity videos? If your output video is quite large, try to find some online tools, for example, https://www.redpandacompress.com to do the video re-codecs and reduce the file size for you might be a good option.

